Embark on an enlightening journey with the Geometry Basics Unit 1 Test! This comprehensive guide unveils the fascinating world of geometry, laying the foundation for your mathematical adventures.
Prepare to delve into the realm of geometric shapes, measurements, transformations, and real-world applications. Uncover the secrets of angles, lines, and symmetry, unlocking the power of geometry in our everyday lives.
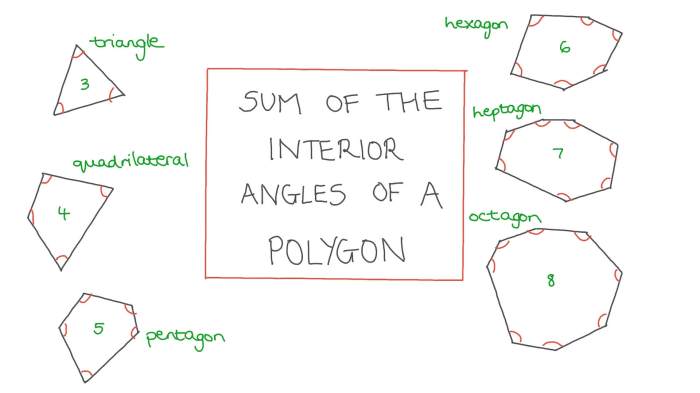
Definitions and Terminology
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of shapes and their spatial relationships.
Some fundamental concepts in geometry include:
- Pointsare dimensionless locations in space.
- Linesare one-dimensional objects that extend infinitely in both directions.
- Planesare two-dimensional objects that extend infinitely in all directions.
- Solidsare three-dimensional objects that have length, width, and height.
Types of Geometric Shapes
There are many different types of geometric shapes, each with its own unique properties.
Some of the most common geometric shapes include:
- Triangleshave three sides and three angles.
- Quadrilateralshave four sides and four angles.
- Circlesare round shapes with no corners or edges.
- Spheresare three-dimensional shapes that are round in all directions.
Geometric Shapes in Everyday Objects
Geometric shapes are all around us in the world. We can see them in buildings, furniture, nature, and even in our own bodies.
Here are a few examples of geometric shapes found in everyday objects:
- The walls of a house are rectangles.
- The wheels of a car are circles.
- The leaves of a tree are ovals.
- The human body is a complex shape that contains many different geometric shapes.
Measuring and Constructing Geometric Figures

Measuring and constructing geometric figures are essential skills in geometry. They allow us to determine the properties of shapes and create accurate representations of them.
Using Rulers, Protractors, and Compasses
Rulers, protractors, and compasses are the primary tools used for measuring and constructing geometric figures.
- Rulersare used to measure the length of line segments and the distance between points.
- Protractorsare used to measure the angles between lines.
- Compassesare used to construct circles and arcs.
Constructing Basic Geometric Shapes
Using rulers, protractors, and compasses, we can construct basic geometric shapes, such as triangles, squares, and circles.
Triangles
To construct a triangle, we need to know the lengths of its sides and the measures of its angles.
Squares
To construct a square, we need to know the length of its sides.
Circles
To construct a circle, we need to know the radius or diameter.
Measuring Angles, Sides, and Areas
Once we have constructed a geometric figure, we can measure its angles, sides, and area.
For the upcoming Geometry Basics Unit 1 test, studying effectively is crucial. If you’re looking for additional support, check out the free CPO test answers 2023 for practice questions and explanations. By utilizing these resources, you’ll enhance your understanding of geometry concepts and boost your confidence for the exam.
Angles
The measure of an angle is expressed in degrees. A protractor is used to measure the angle.
Sides
The length of a side is expressed in units of length. A ruler is used to measure the side.
Areas
The area of a figure is expressed in square units. The formula for the area of a figure depends on the shape of the figure.
Relationships Between Geometric Figures

Geometric figures can have various relationships with each other. These relationships include congruence, similarity, and symmetry.
Congruence
Congruent shapes are shapes that have the same size and shape. They have the same measurements and angles. For example, two squares with side lengths of 5 cm are congruent.
Similarity
Similar shapes have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. They have the same angles but different side lengths. For example, two triangles with the same angles but different side lengths are similar.
Symmetry
Symmetry refers to the balance and proportion of a figure. A figure has symmetry if it can be divided into two or more equal parts that are mirror images of each other. Symmetry is often used in art and design to create aesthetically pleasing objects.
Transformations of Geometric Figures

Geometric transformations are operations that move or change the shape and size of geometric figures without altering their fundamental properties. These transformations include translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations.
Translations
A translation moves a figure from one point to another without changing its size or shape. To perform a translation, choose a direction and distance, then move the figure in that direction by that distance.
Rotations
A rotation turns a figure around a fixed point called the center of rotation. The amount of rotation is measured in degrees. To perform a rotation, choose a center of rotation and an angle of rotation, then rotate the figure around the center by that angle.
Reflections
A reflection flips a figure over a line called the line of reflection. To perform a reflection, choose a line of reflection, then flip the figure over that line.
Dilations
A dilation changes the size of a figure by a certain factor called the scale factor. To perform a dilation, choose a center of dilation and a scale factor, then multiply the coordinates of each point in the figure by the scale factor.
Real-World Applications
Geometric transformations have many real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: Designing buildings and structures
- Engineering: Designing bridges, cars, and other objects
- Computer graphics: Creating 3D models and animations
- Robotics: Controlling the movement of robots
Coordinate Geometry: Geometry Basics Unit 1 Test
Coordinate geometry is a branch of geometry that uses a coordinate system to represent and analyze geometric figures and relationships. It provides a systematic and precise way to describe and manipulate geometric objects.
The coordinate plane is a two-dimensional plane divided into four quadrants by two perpendicular lines, the x-axis and the y-axis. Each point on the coordinate plane is represented by an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. The first number is the x-coordinate, which represents the distance from the y-axis, and the second number is the y-coordinate, which represents the distance from the x-axis.
Plotting Points and Graphing Lines
To plot a point on the coordinate plane, locate the point’s x-coordinate on the x-axis and move up or down by the y-coordinate. To graph a line, plot at least two points on the line and connect them with a straight line.
Equations of Lines
The equation of a line is an algebraic equation that represents all the points on the line. The most common form of a linear equation is the slope-intercept form, which is written as y = mx + b, where m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept.
The slope of a line is a measure of its steepness. A positive slope indicates that the line rises from left to right, while a negative slope indicates that the line falls from left to right. The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
Applications of Geometry in Real-World Contexts
Geometry is not just a subject confined to textbooks and classrooms; it finds practical applications in various fields, shaping our world in countless ways. From designing majestic buildings to constructing sturdy bridges and creating captivating art, geometry plays a pivotal role.
Architecture, Geometry basics unit 1 test
In architecture, geometry serves as the foundation for designing and constructing buildings that are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound. Architects utilize geometric principles to create blueprints, ensuring the stability, functionality, and visual appeal of structures. For instance, the iconic triangular shape of the Eiffel Tower provides exceptional stability against wind forces, while the intricate geometric patterns in Gothic cathedrals create a sense of awe and grandeur.
Engineering
Geometry is indispensable in engineering disciplines. Engineers rely on geometric principles to design and construct bridges, roads, and other infrastructure. The geometric shapes of bridges, such as arches and suspension cables, determine their load-bearing capacity and resistance to external forces.
Similarly, the precise measurements and angles used in road construction ensure smooth and efficient transportation.
Art and Design
Geometry also plays a significant role in the realm of art and design. Artists use geometric shapes and patterns to create visually appealing and meaningful works. From the geometric abstractions of Piet Mondrian to the intricate tessellations of Islamic art, geometry provides a framework for artistic expression.
Designers utilize geometric principles to create visually balanced and harmonious compositions, enhancing the aesthetics of products, interiors, and graphic designs.
FAQ Resource
What is geometry?
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the properties, measurement, and relationships of points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids.
What are the different types of geometric shapes?
There are many different types of geometric shapes, including triangles, squares, circles, cubes, and spheres.
How can I measure geometric figures?
You can measure geometric figures using tools such as rulers, protractors, and compasses.
What are geometric transformations?
Geometric transformations are operations that move or change geometric figures without changing their size or shape.
How is geometry used in the real world?
Geometry is used in many different fields, including architecture, engineering, art, and design.