Chapter 6 Section 1 Price Controls Worksheet Answers: An In-Depth Exploration delves into the intricate world of price controls, examining their objectives, types, effects, and real-world applications. This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of this critical economic concept, offering insights into its impact on consumers, producers, and the overall economy.
As we delve into the topic, we will explore the arguments for and against price controls, weighing the potential benefits against the possible drawbacks. Through detailed examples and expert analysis, we will gain a nuanced understanding of the effectiveness of price controls in various contexts, shedding light on their complexities and implications.
Price Controls: Chapter 6 Section 1 Price Controls Worksheet Answers

Price controls are government-imposed regulations that limit the prices of goods and services. Their objectives include protecting consumers from excessive pricing, stabilizing prices during periods of inflation, and ensuring access to essential goods for low-income households.
Types of price controls include:
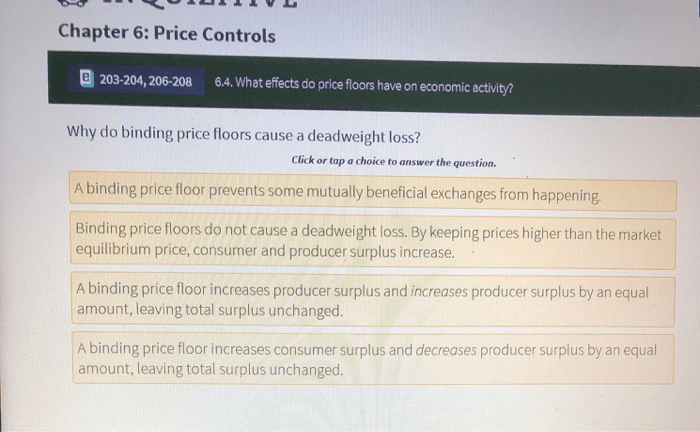
- Price ceilings: Set a maximum price for a good or service.
- Price floors: Set a minimum price for a good or service.
- Wage and rent controls: Limit the prices of labor and housing, respectively.
Effects of Price Controls
Impact on Consumers
Price ceilings can lower prices for consumers, making goods and services more affordable. However, they can also lead to shortages as producers are discouraged from supplying goods at the controlled price.
Impact on Producers
Price floors can benefit producers by ensuring a minimum price for their products. However, they can also lead to surpluses as consumers are less likely to purchase goods at the higher price.
Price Controls in Practice
Many countries have implemented price controls, including:
- India: Price controls on essential commodities such as sugar and wheat.
- Venezuela: Price controls on a wide range of goods and services, leading to severe shortages.
- United States: Rent control in some cities, with varying levels of effectiveness.
Arguments For and Against Price Controls, Chapter 6 section 1 price controls worksheet answers
Arguments in Favor
Price controls can protect consumers from exploitation, stabilize prices, and ensure access to essential goods.
Arguments Against
Price controls can lead to shortages, surpluses, black markets, and reduced economic efficiency. They can also discourage investment and innovation.
Query Resolution
What are the primary objectives of price controls?
Price controls aim to achieve various objectives, including protecting consumers from excessive prices, ensuring fair competition, stabilizing markets, and addressing perceived market failures.
How do price controls affect consumers?
Price controls can impact consumers positively by lowering prices and protecting them from exploitation. However, they can also lead to shortages, reduced product quality, and limited choice.
What are the potential consequences of price controls for producers?
Price controls can have significant consequences for producers, potentially reducing their profits, discouraging investment, and limiting their ability to respond to market demands.