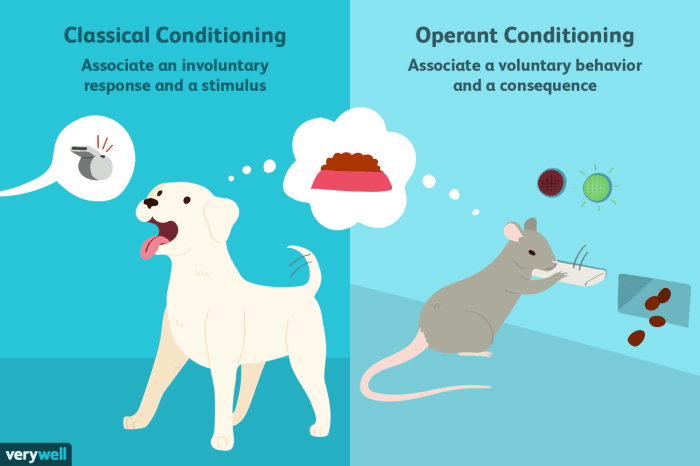
Delving into the realm of learning and behavior, the classical and operant conditioning worksheet serves as an invaluable tool for comprehending the fundamental principles that govern how we interact with our environment. This comprehensive guide will provide a thorough exploration of both classical and operant conditioning, offering practical examples and engaging worksheets to enhance understanding.
Through this exploration, we will uncover the intricacies of how stimuli and responses shape our behaviors, shedding light on the mechanisms that underlie learning and motivation. By harnessing the power of these conditioning techniques, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their own behaviors and the behaviors of others, empowering them to make informed choices and foster positive change.
Classical Conditioning: Classical And Operant Conditioning Worksheet
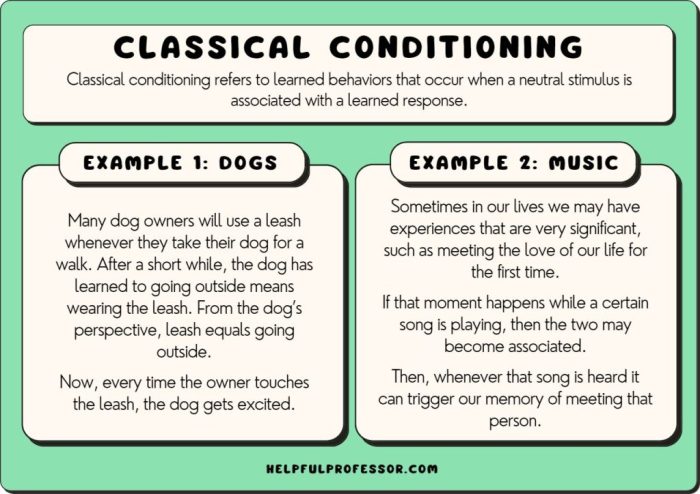
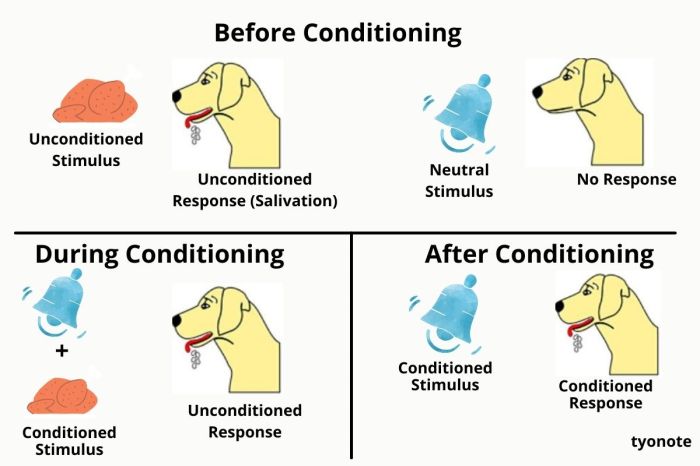
Classical conditioning, also known as Pavlovian conditioning, is a learning process that involves associating a neutral stimulus with a meaningful stimulus. Over time, the neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus and triggers a conditioned response. This type of conditioning is based on the principles of classical conditioning, which were first proposed by Ivan Pavlov in the early 20th century.
Principles of Classical Conditioning
- Unconditioned Stimulus (US):A naturally occurring stimulus that triggers an unconditioned response.
- Unconditioned Response (UR):An automatic and innate response to an unconditioned stimulus.
- Neutral Stimulus (NS):A stimulus that does not initially trigger a response.
- Conditioned Stimulus (CS):A neutral stimulus that, after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus, triggers a conditioned response.
- Conditioned Response (CR):A learned response to a conditioned stimulus.
Examples of Classical Conditioning in Everyday Life, Classical and operant conditioning worksheet
- Dog salivating at the sound of a bell:The sound of the bell (CS) was initially a neutral stimulus, but after being paired with the presentation of food (US), it became a conditioned stimulus that triggered salivation (CR).
- Fear of spiders:A spider (US) naturally triggers a fear response (UR). If a person is repeatedly exposed to spiders while also experiencing something negative, such as a loud noise (NS), the loud noise can become a conditioned stimulus that triggers fear (CR) even in the absence of a spider.
Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a learning process that involves modifying behavior by reinforcing or punishing specific actions. This type of conditioning is based on the principles of operant conditioning, which were first proposed by B.F. Skinner in the mid-20th century.
Principles of Operant Conditioning
- Positive Reinforcement:Adding a pleasant consequence to increase the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
- Negative Reinforcement:Removing an unpleasant consequence to increase the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
- Punishment:Adding an unpleasant consequence or removing a pleasant consequence to decrease the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
- Extinction:Removing the reinforcement or punishment associated with a behavior, leading to a decrease in the behavior’s frequency.
Examples of Operant Conditioning in Everyday Life
- Rewarding a child for good behavior:Giving a child a treat or praise (positive reinforcement) for completing their homework increases the likelihood of them completing their homework in the future.
- Grounding a child for misbehaving:Removing a privilege (negative reinforcement) for misbehaving decreases the likelihood of the child misbehaving in the future.
FAQ Summary
What are the key differences between classical and operant conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves the association of two stimuli, while operant conditioning focuses on the consequences of behavior.
How can I use classical and operant conditioning to improve my study habits?
Classical conditioning can be used to create positive associations with studying, while operant conditioning can be used to reinforce desired study behaviors.
What are some common applications of classical and operant conditioning in everyday life?
Classical conditioning is used in advertising, while operant conditioning is used in training animals and children.