Guillain barre syndrome hesi case study – The Guillain-Barre Syndrome HESI case study offers a comprehensive exploration of this complex neurological disorder. Delving into its clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, management strategies, and nursing considerations, this study provides invaluable insights for healthcare professionals.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. Characterized by progressive muscle weakness and sensory loss, GBS can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Introduction
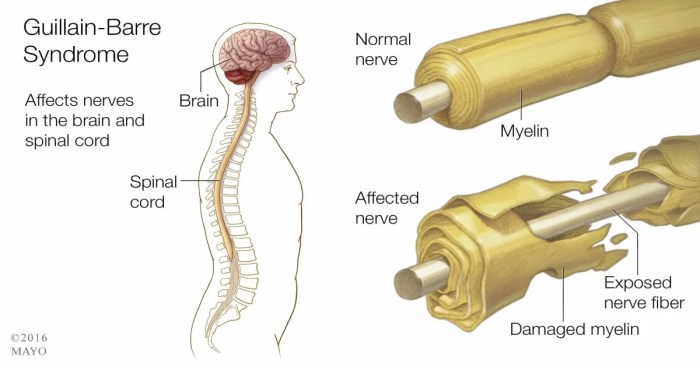
Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It is characterized by rapidly progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an infection, such as a recent bout of gastroenteritis or the flu.
The HESI case study on GBS provides a detailed overview of the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of this condition.
Clinical Manifestations
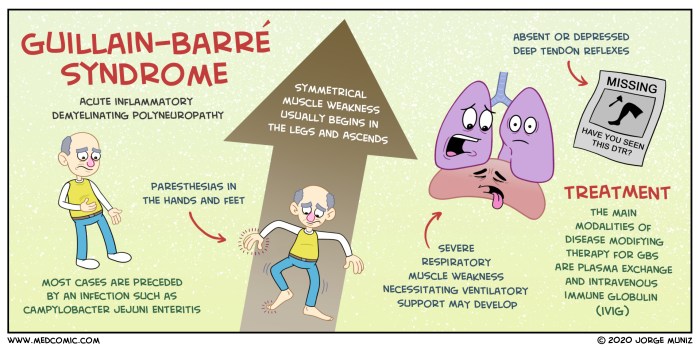
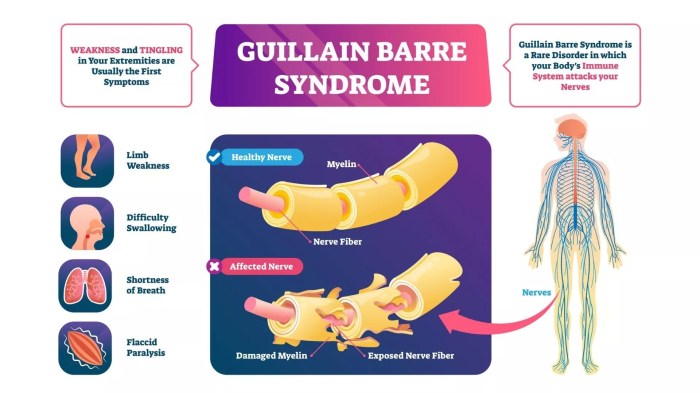
The symptoms of GBS typically begin with weakness in the legs, which progresses to involve the arms and respiratory muscles. In severe cases, GBS can lead to paralysis of all four limbs, as well as the muscles that control breathing and swallowing.
Other symptoms of GBS may include numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, difficulty with speech and vision, and bladder and bowel incontinence.
Pathophysiology, Guillain barre syndrome hesi case study
GBS is caused by an autoimmune response that leads to damage to the peripheral nerves. The immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath, which is the protective covering of the nerves. This damage disrupts the transmission of nerve signals, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis.
Management and Treatment
The treatment of GBS is supportive and aims to manage the symptoms and prevent complications. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and plasmapheresis are the two main treatments for GBS. IVIG is a blood product that contains antibodies that help to suppress the immune system.
Plasmapheresis is a procedure that removes the antibodies from the blood.
Nursing Considerations
Nurses play a vital role in the care of patients with GBS. They are responsible for assessing the patient’s symptoms, monitoring their progress, and providing supportive care. Nurses also play a key role in patient education and support.
Case Study Analysis
The HESI case study on GBS presents a patient with rapidly progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. The patient’s history, physical examination, and laboratory findings are consistent with the diagnosis of GBS. The differential diagnosis includes other conditions that can cause muscle weakness and paralysis, such as myasthenia gravis and botulism.
Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support are essential components of the care of patients with GBS. Patients need to be informed about the condition, its treatment, and its prognosis. They also need to be provided with support and resources to help them cope with the challenges of living with GBS.
FAQ Explained: Guillain Barre Syndrome Hesi Case Study
What are the initial symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
GBS typically presents with weakness and tingling in the lower extremities that progresses to involve the upper extremities and respiratory muscles.
How is Guillain-Barre Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical examination, nerve conduction studies, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
What is the primary treatment for Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and plasmapheresis are the primary treatments for GBS, aimed at suppressing the autoimmune response.